Ansible Sensor Health Check Playbook
.jpg)
If you do not have an Ansible console host setup, please follow these guides to install and set up your inventory, config, and vault.
1. Project Overview
This project involves an Ansible playbook designed to monitor the health of network sensor services, including Zeek, Tcpdump, and Snort, on all targeted hosts (Can be whatever serivce you would like). Additionally, it checks disk usage to identify potential storage issues that could affect sensor performance (Log rotate not occuring). The playbook ensures these critical network monitoring tools are operational and flags any disk space constraints.
- Objective: Automate health checks for network sensor services and disk usage to ensure continuous network monitoring.
- Requirements: Ansible 2.9+, Linux systems with systemd, Zeek, Tcpdump, and Snort installed.
- Hardware Used: Linux-based servers hosting network sensor services.
- Software Used: Ansible, systemd, standard Linux utilities (df, find).
- Skills Learned: Ansible automation, service monitoring, disk usage analysis, secure playbook execution.
2. Script Breakdown and Monitoring Relevance
Security Note: Always review playbooks before execution. Use Ansible Vault to secure sensitive data like the sensors_pwd variable.
2.1 Zeek Service Check
Relevance: Ensures Zeek, a network analysis framework, is running to provide continuous traffic monitoring and protocol analysis.
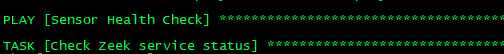
- name: Check Zeek service status
ansible.builtin.systemd:
name: zeek
state: started
become: yes
become_user: root
become_method: sudo
register: zeek_status
ignore_errors: yes
changed_when: false
- name: Display Zeek status
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: "Zeek is {{ 'running' if zeek_status.status.ActiveState == 'active' else 'not running' }}"
when: zeek_status.status is defined
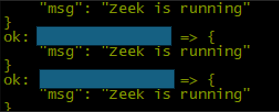
2.2 Tcpdump Service Check
Relevance: Verifies that Tcpdump is actively capturing network packets, essential for detailed traffic analysis and troubleshooting.
- name: Check Tcpdump service status
ansible.builtin.systemd:
name: tcpdump
state: started
become: yes
become_user: root
become_method: sudo
register: tcpdump_status
ignore_errors: yes
changed_when: false
- name: Display Tcpdump status
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: "Tcpdump is {{ 'running' if tcpdump_status.status.ActiveState == 'active' else 'not running' }}"
when: tcpdump_status.status is defined
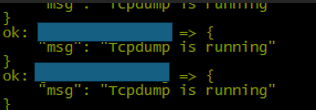
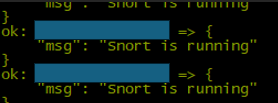
2.3 Snort Service Check
Relevance: Confirms Snort, an intrusion detection system, is operational to detect and alert on potential network threats.
- name: Check Snort service status
ansible.builtin.systemd:
name: snort
state: started
become: yes
become_user: root
become_method: sudo
register: snort_status
ignore_errors: yes
changed_when: false
- name: Display Snort status
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: "Snort is {{ 'running' if snort_status.status.ActiveState == 'active' else 'not running' }}"
when: snort_status.status is defined
2.4 Disk Usage Monitoring
Relevance: Identifies 100% full filesystems and large files, which can disrupt sensor operations by preventing data storage or logging.
- name: Check disk usage
ansible.builtin.command: df -h
become: yes
become_user: root
become_method: sudo
register: disk_usage
changed_when: false
failed_when: false
- name: Parse disk usage for 100% full filesystems
ansible.builtin.set_fact:
full_disks: "{{ disk_usage.stdout_lines | select('match', '.*100%.*') | list }}"
no_log: true
- name: Display 100% full filesystems
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: "{{ item }}"
loop: "{{ full_disks }}"
when: full_disks | length > 0
- name: Find large files on 100% full filesystems
ansible.builtin.command: find / -xdev -type f -size +100M -exec ls -lah {} + | sort -hr -k 5 | head -n 5
become: yes
become_user: root
become_method: sudo
register: large_files
changed_when: false
failed_when: false
when: full_disks | length > 0
- name: Display large files
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: "{{ item }}"
loop: "{{ large_files.stdout_lines }}"
when: large_files.stdout_lines is defined and full_disks | length > 0
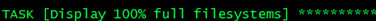
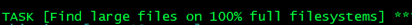
3. Tips and Lessons Learned
Practical advice and insights gained from developing the playbook:
- Tip 1: Secure the
sensors_pwdvariable using Ansible Vault to prevent unauthorized access. - Tip 2: Use
ignore_errors: yesto ensure the playbook continues even if a service check fails. - Tip 3: Run the playbook on a schedule (e.g., via cron or Ansible Tower) for proactive monitoring.
- Lesson Learned: Full disks can significantly impact network sensors, halting packet capture or alert generation.
- Future Improvements: Integrate alerts (e.g., email or Slack) for service failures or disk issues.
4. Conclusion
This Ansible playbook offers a reliable method for monitoring network sensor services and disk usage across multiple hosts. Its robust error handling and modular structure make it ideal for maintaining network security monitoring systems. Future enhancements could include automated recovery tasks or integration with external monitoring tools.
5. Full Code
Security Note: Always review code before executing. Ensure sensitive data is encrypted using Ansible Vault.
---
- name: Sensor Health Check
hosts: all
gather_facts: no
vars:
ansible_vault_password_file: "{{ sensors_pwd }}"
tasks:
- name: Check Zeek service status
ansible.builtin.systemd:
name: zeek
state: started
become: yes
become_user: root
become_method: sudo
register: zeek_status
ignore_errors: yes
changed_when: false
- name: Display Zeek status
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: "Zeek is {{ 'running' if zeek_status.status.ActiveState == 'active' else 'not running' }}"
when: zeek_status.status is defined
- name: Check Tcpdump service status
ansible.builtin.systemd:
name: tcpdump
state: started
become: yes
become_user: root
become_method: sudo
register: tcpdump_status
ignore_errors: yes
changed_when: false
- name: Display Tcpdump status
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: "Tcpdump is {{ 'running' if tcpdump_status.status.ActiveState == 'active' else 'not running' }}"
when: tcpdump_status.status is defined
- name: Check Snort service status
ansible.builtin.systemd:
name: snort
state: started
become: yes
become_user: root
become_method: sudo
register: snort_status
ignore_errors: yes
changed_when: false
- name: Display Snort status
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: "Snort is {{ 'running' if snort_status.status.ActiveState == 'active' else 'not running' }}"
when: snort_status.status is defined
- name: Check disk usage
ansible.builtin.command: df -h
become: yes
become_user: root
become_method: sudo
register: disk_usage
changed_when: false
failed_when: false
- name: Parse disk usage for 100% full filesystems
ansible.builtin.set_fact:
full_disks: "{{ disk_usage.stdout_lines | select('match', '.*100%.*') | list }}"
no_log: true
- name: Display 100% full filesystems
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: "{{ item }}"
loop: "{{ full_disks }}"
when: full_disks | length > 0
- name: Find large files on 100% full filesystems
ansible.builtin.command: find / -xdev -type f -size +100M -exec ls -lah {} + | sort -hr -k 5 | head -n 5
become: yes
become_user: root
become_method: sudo
register: large_files
changed_when: false
failed_when: false
when: full_disks | length > 0
- name: Display large files
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: "{{ item }}"
loop: "{{ large_files.stdout_lines }}"
when: large_files.stdout_lines is defined and full_disks | length > 0